Objective
caution
This page has been moved to the eSSIF-Lab Framework on Github.
Short Description
An Objective is something toward which a party (its owner) directs effort (an aim, goal, or end of action). Typically, the realization of an objective can be observed in terms of results, e.g. products that have been produced, services that are being provided, a situation or state (e.g. happiness) that has been continued etc. A party that has an objective does not necessarily produce these results itself; it may also seek to realize them in order to use (consume) them. Production and consumption of results are the two different perspectives from which an objective can be perceived.
Ownership of the objective is implied, as it is part of that party's knowledge (which is owned by that party). Consequently, a single objective cannot be shared, as it would imply it had multiple owners.In order to communicate its objectives, a party typically uses a text - a description of its intention, the aim, the goal, etc. In practice, people are known to confuse this description with the objective itself, which may cause them to think that two parties shared the same objective becasue these parties happen to use the same descriptive text. As mentioned before, that's not possible. However, it may be the case that two parties each have an objective that is similar to a very high degree. However, as each party can autonomously change the descriptive text, (the specification of) the results and any other attributes, it is obvious that what might seem to be the same objective is actually a set of (very) similar objectives.
We refer you to the Governance and Management pattern for a description of how to think about objectives in contexts where there are multiple parties.
Purpose
The ability to distinguish between (non)objectives is relevant as objectives are the drivers behind the reasoning and decisions that parties make, the policies and working instructions that they specify so that its agents know what to do, when to do it, and how to do it. Moreover, objectives are 1-1 associated with risks. Finally, objectives must be known in order to obtain (personal) data according to the GDPR.
Criterion
An objective is something
- that is owned by a single party;
- toward which its owner directs its efforts: an aim, goal, or end of action - this action is related to the the owner producing the associated results (management) and/or consuming the results (governance);
- that can be realized, and this realization can be seen in terms as the coming into existence of results (e.g. products, services, a situation or state (e.g. happiness));
- that may have a description (text, that represents and identifies the objective within the knowledge of its owner)
Examples
- generically: anything that, according to a party c.q. its way of thinking, is important to be realized or maintained, qualifies as an Objective (and identifies its owner as that party).
- most people have an objective that could be described as "to stay alive".
- the equivalent in organizations is 'continuation of its existence' (many operate 'business-continuity processes' to realize this, and to identify and mitigate any associated risks).
Formalization
Here is a visual representation of the formalization of this concept, using the following notations and conventions:
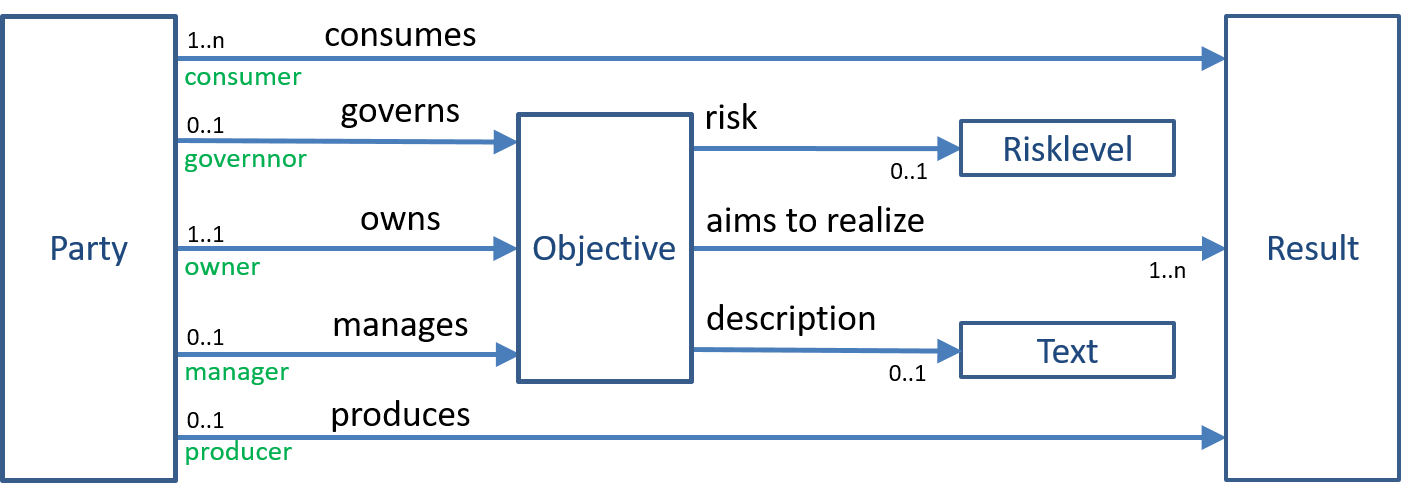
Figure 1. Parties and their objectives.
The figure shows that every objective has a single owner, which is the party that aims to realize the associated result(s).
This party may describe the objective, typically in terms of a text (or speech), using its own wording. This description identifies the objective in the context/knowledge of its owner, implying that it may be misinterpreted by others. In particular (and specifically if the description is limited to a single phrase/sentence), parties may (or may not) be right in thinking they have a similar objective, or even erroneously think they share that objective in the sense that they both own the objective, which is not possible in this way of thinking.
Whether or not an objective is realised should be determinable, also by other parties, by the results that must (continue to) exist. Such results can be products that have been produced, services that are (continuously) being provided, a situation or state (e.g. happiness) that has been continued etc. Results are typically auditable, and depending on the kind of result an auditor might establish their existence (and as the case may be: their (proper) design and/or operation). But it is not necessarily the owner of the objective that has produced them, as we shall see.
An objective can be seen from two different perspectives. In the governance perspective, a party ensures that the associated results become (or remain) available so that the party can actually use them. In this perspective, a party does not care who produces the results, nor how they are being produced. We say that the party governs the objective, and will be consuming the associated results. In this governance perspective, a party will typically determine which (possibly other) party will be producing (and/or providing it with) these results. Also, it may think of a fallback scenario, e.g. select alternative producers it may contact in case the producer fails to deliver. However, it can (try to) communicate with the producing party, and see if the properties of the results it requires (so that they are fit for the purposes for which they are going to be used) match the properties of the results that are provided.
In the management perspective, a party ensures that the associated results become (or remain) available by producing them (or obtaining them in some other way), and making them available to (possibly) other parties that will be using them. This means planning (of budgets and other resources, timelines, etc.), specifying the results that it will be producing, organizing (the efficiency of) the actual production, instructing its agents that do the actual production, etc. Managing these results also includes marketing thereof, trying to find parties that will actually want to use them. And it can communicate with (prospective) consumers, and see if the properties of the results it will be producing match the properties required by its customers.
For more information, e.g. about how different parties interact in their roles of producer and consumer, we refer you to the Governance and Management pattern.